|
001 |
The definitions of some objects, including views and procedures,
reference other objects, such as tables. As a result, the objects being
defined are dependent on the objects referenced in their definitions.
This chapter discusses the dependencies among schema objects and how
Oracle automatically tracks and manages these dependencies.
|
某些数据库对象(例如视图,过程)的定义中可能会引用其他对象(例如数据表)。因此这样的数据库对象将依赖于其定义中所引用的对象。本章将讨论方案对象(schema
object)的依赖性(dependency),以及 Oracle 如何自动地跟踪与管理依赖性。
|
|
002 |
This chapter contains the following topics:
|
本章包含以下主题: |
|
003 |
Introduction to
Dependency Issues
|
6.1 依赖性简介
|
|
004 |
Some types of schema objects can reference other objects as part of
their definition. For example, a view is defined by a query that
references tables or other views. A procedure's body can include SQL
statements that reference other objects of a database. An object that
references another object as part of its definition is called a
dependent object, while the object being referenced is a referenced
object. Figure 6-1 illustrates the
different types of dependent and referenced objects:
|
某些类型的方案对象(schema
object)可以在其定义中引用其他对象。例如,视图的定义就是一个引用了其他表或视图的查询;一个过程中也可以包含引用了其他数据库对象的 SQL
语句。如果一个对象的定义中引用了其他对象,那么此对象被称为依赖对象(dependent object),此对象所引用的对象被称为引用对象(referenced
object)。图6-1 显示了各种类型的依赖对象和引用对象:
|
|
005 |
Figure 6-1 Types of Possible
Dependent and Referenced Schema Objects
|
图6-1 各种类型的依赖对象与引用对象 |
|
006 |

|

|
|
007 |
Figure 6-1 lists the following Dependent Objects:
- Table
- View
- Procedure
- Function
- Package Specification
- Package Body
- Database Trigger
- User-Defined Object and Collection Types
This illustration also lists the following Referenced Objects:
- Table
- View
- Sequence
- Synonym
- Procedure
- Function
- Package Specification
- User-Defined Object and Collection Types
|
图6-1 列出了以下依赖对象:
- 表
- 视图
- 过程
- 函数
- 包声明
- 包定义
- 触发器
- 用户定义对象和集合类型
本图还列出了一下引用对象:
- 表
- 视图
- 序列
- 同义词
- 过程
- 函数
- 包定义
- 用户定义对象和集合类型
|
|
008 |
If you alter the definition of a referenced object, dependent objects
may or may not continue to function without error, depending on the type
of alteration. For example, if you drop a table, no view based on the
dropped table is usable.
|
如果用户修改(alter)了一个引用对象(referenced object)的定义,则相应的依赖对象(dependent
object)是否能够正常工作将取决于修改的类型。例如,当用户移除(drop)了一个表,则所有基于此表的视图将失效。
|
|
009 |
Oracle automatically records dependencies among objects to alleviate the
complex job of dependency management for the database administrator and
users. For example, if you alter a table on which several stored
procedures depend, Oracle automatically recompiles the dependent
procedures the next time the procedures are referenced (run or compiled
against).
|
Oracle
能够自动地记录对象间的依赖关系,以便降低依赖性管理的复杂程度,减轻数据库管理员和用户的工作负担。例如,一个表被多个过程所引用,当用户修改了引用表(referenced
table)的定义后,Oracle 将在依赖过程(dependent
procedure)下一次被引用时自动地将其重新编译(recompile)。
|
|
010 |
To manage dependencies among schema objects, all of the schema objects
in a database have a status:
- Valid schema objects have been
compiled and can be immediately used when referenced.
- Invalid schema objects must be
compiled before they can be used.
- For procedures, functions, and packages, this means compiling the
schema object.
- For views, this means that the view must be reparsed, using the
current definition in the data dictionary.
|
为了管理方案对象(schema object)间的依赖关系,Oracle 需要记录所有的方案的状态(status):
- 有效的(valid)已经通过编译,可以在被引用时直接使用。
- 无效的(invalid)必须在使用之前进行编译。
- 对于过程,函数和包来说,这意味着对其进行编译
- 对于视图来说,这意味着此视图必须使用引用对象(referenced
object)当前在数据字典中的定义信息重新进行语法分析(parse)。
|
|
011 |
Only dependent objects can be invalid. Tables, sequences, and synonyms
are always valid.
|
只有依赖对象(dependent object)可以处于无效状态(invalid)。表,序列,和同义词总是处于有效状态(valid)。
|
|
012 |
If a view, procedure, function, or package is invalid, Oracle may have
attempted to compile it, but errors relating to the object occurred. For
example, when compiling a view, one of its base tables might not exist,
or the correct privileges for the base table might not be present. When
compiling a package, there might be a PL/SQL or SQL syntax error, or the
correct privileges for a referenced object might not be present. Schema
objects with such problems remain invalid.
|
如果一个视图,过程,函数或包处于无效状态,Oracle
将会尝试对其进行重新编译,但这个过程可能会发生错误。例如,当编译一个视图时,此视图的基表(base
table)有可能不存在,或访问基表的权限不存在;当编译一个包时,有可能出现 PL/SQL 或 SQL
语法错误,或访问引用对象(referenced object)的权限不存在。在编译时发生此类问题的方案对象(schema
object)将保持无效状态(invalid)。
|
|
013 |
Oracle automatically tracks specific changes in the database and records
the appropriate status for related objects in the data dictionary.
|
Oracle 能够自动地跟踪数据库中发生的特定变化,并在数据字典(data dictionary)中记录相关的方案对象(schema
object)的最新状态。
|
|
014 |
Status recording is a recursive process. Any change in the status of a
referenced object changes the status not only for directly dependent
objects, but also for indirectly dependent objects.
|
状态记录是一个递归的过程。引用对象(referenced object)的状态变化不仅会导致其直接依赖对象(directly dependent
object)的状态变化,同时会影响其间接依赖对象(indirectly dependent object)的状态。
|
|
015 |
For example, consider a stored procedure that directly references a
view. In effect, the stored procedure indirectly references the base
tables of that view. Therefore, if you alter a base table, the view is
invalidated, which then invalidates the stored procedure.
Figure 6-2 illustrates indirect
dependencies:
|
例如,当一个存储过程直接引用了一个视图时,则其间接上引用了此视图的基表(base
table)。因此,当用户修改(alter)了基表后,视图将处于无效状态,同时也将导致存储过程处于无效状态。图6-2
显示了这种间接依赖性(indirect dependency)。 |
|
016 |
Figure 6-2 Indirect
Dependencies
|
图6-2 间接依赖性 |
|
017 |
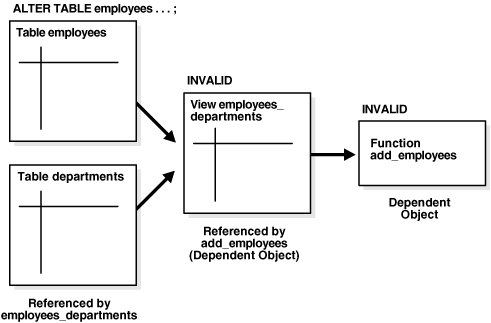
|

|
|
018 |
Figure 6-2 shows indirect dependencies. In the center
of the picture is a view called employees_departments that
references two base tables, employees and departments (shown to the
left).
The view employees_departments is referenced by a function
add_employees (on the right), making add_employees a dependent
object, dependent on the view employees_departments. Any changes to
the referenced tables, employees or departments, invalidate the view
employees_departments. When employees_dependents becomes invalid, so
does its dependent object, the function add_employees.
|
图6-2 显示了间接依赖性。此图的中间是名为 employees_departments
的视图,她引用了两个基表,employees 和 departments(见图左侧)。
视图 employees_departments 由函数 add_employees 所引用(见图右侧),这使 add_employees
成为一个依赖对象,她依赖于视图 employees_departments。基表 employees 或 departments
的任何改变,都将使 employees_departments 视图处于无效状态。当 employees_departments
无效后,其依赖对象 add_employees 函数也将处于无效状态。
|
|
019 |
Resolution of
Schema Object Dependencies
|
6.2 解析方案对象的依赖性
|
|
020 |
When a schema object is referenced directly in a SQL statement or
indirectly through a reference to a dependent object, Oracle checks the
status of the object explicitly specified in the SQL statement and any
referenced objects, as necessary. Oracle's action depends on the status
of the objects that are directly and indirectly referenced in a SQL
statement:
- If every referenced object is valid,
then Oracle runs the SQL statement immediately without any
additional work.
- If any referenced view or PL/SQL
program unit (procedure, function, or package) is invalid, then
Oracle automatically attempts to compile the object.
- If all invalid referenced objects can
be compiled successfully, then they are compiled and Oracle runs the
SQL statement.
- If an invalid object cannot be
compiled successfully, then it remains invalid. Oracle returns an
error and rolls back the failing SQL statement. The rest of the
transaction is unaltered and can be committed or rolled back by the
user.
|
当一个方案对象(schema object)在 SQL 语句中被直接引用或被此语句中的依赖对象(dependent
object)所引用(间接引用)时,Oracle 均会在需要时对其状态进行检查。SQL 语句中被直接或间接引用的对象的状态决定了 Oracle
的后续操作:
- 如果 SQL 语句中所有的引用对象(referenced
object)均处于有效状态,则 Oracle 无需进行其他工作就可以直接执行 SQL 语句。
- 如果 SQL 语句中存在无效的引用(referenced)视图或
PL/SQL 程序结构(过程,函数,或包),Oracle 将自动地尝试编译这些对象。
- 如果所有无效的引用对象都能被成功编译,则 Oracle 将在编译后执行
SQL 语句。
- 如果一个方案对象不能被成功编译,那么她将继续保持无效状态。Oracle
回滚执行失败的 SQL 语句并返回一个错误信息。事务中已成功的操作由用户决定是进行提交还是回滚。
|
|
021 |
Note:
Oracle attempts to recompile an invalid object dynamically only if
it has not been replaced since it was detected as invalid. This
optimization eliminates unnecessary recompilations.
|
提示:
如果一个方案对象在处于无效状态之后被用户替换(replace),则
Oracle 不会对其进行重新编译。这项优化措施减少了不必要的重新编译操作。
|
|
022 |
Compilation of Views and PL/SQL Program Units
|
6.2.1 编译视图及 PL/SQL 程序结构
|
|
023 |
A view or PL/SQL program unit can be compiled and made valid if the
following conditions are satisfied:
- The definition of the view or program
unit must be correct. All of the SQL and PL/SQL statements must be
proper constructs.
- All referenced objects must be present
and of the expected structure. For example, if the defining query of
a view includes a column, the column must be present in the base
table.
- The owner of the view or program unit
must have the necessary privileges for the referenced objects. For
example, if a SQL statement in a procedure inserts a row into a
table, the owner of the procedure must have the
INSERT privilege for the referenced
table.
|
当满足以下条件时,视图及 PL/SQL 程序结构可以被编译并置为有效状态:
- 视图或 PL/SQL 程序结构的定义必须正确。SQL 及 PL/SQL
语句的语法结构必须正确。
- 所有引用对象(referenced
object)及其结构必须满足定义的要求。例如,如果视图的定义查询(defining
query)中引用了某列,那么此列必须存在于基表(base table)中。
- 视图或 PL/SQL
程序结构的所有者必须具备访问引用对象的权限。例如,过程中的一个 SQL
语句向某个表中插入一条数据,那么此过程的所有者必须具备对引用表(referenced table)的
INSERT 权限。
|
|
024 |
Views and Base Tables
|
6.2.1.1 视图和基表
|
|
025 |
A view depends on the base tables or views referenced in its defining
query. If the defining query of a view is not explicit about which
columns are referenced, for example, SELECT * FROM
table, then the defining query is expanded when stored in the
data dictionary to include all columns in the referenced base table at
that time.
|
一个视图依赖于在其定义查询(defining query)中所引用的基表(base
table)及其他视图。如果视图的定义查询中没有显式地说明引用哪些列,例如使用了 SELECT * FROM
table 语句,那么 Oracle 在存储此定义查询时将引用基表中的全部列。
|
|
026 |
If a base table or view of a view is altered, renamed, or dropped, then
the view is invalidated, but its definition remains in the data
dictionary along with the privileges, synonyms, other objects, and other
views that reference the invalid view.
|
如果一个视图所引用的基表(base
table)或其他视图被修改(alter),重命名(rename)或移除(drop)后,此视图将被置为无效状态,但其定义仍被保存于数据字典内,相关的权限信息,引用此视图的同义词,对象,及其他视图也
都会被保留。
|
|
027 |
Note:
Whenever you create a table, index, and view, and then drop the
table, all objects dependent on that table are invalidated,
including views, packages, package bodies, functions, and
procedures.
|
提示:
当用户创建了表,索引,视图后,再将表移除(drop),所有依赖于被移除表的对象都将被置于无效状态,这些对象包括视图,包,包定义,函数,和过程。
|
|
028 |
An attempt to use an invalid view automatically causes Oracle to
recompile the view dynamically. After replacing the view, the view might
be valid or invalid, depending on the following conditions:
- All base tables referenced by the
defining query of a view must exist. If a base table of a view is
renamed or dropped, the view is invalidated and cannot be used.
References to invalid views cause the referencing statement to fail.
The view can be compiled only if the base table is renamed to its
original name or the base table is re-created.
- If a base table is altered or
re-created with the same columns, but the datatype of one or more
columns in the base table is changed, then most dependent views can
be recompiled successfully.
- If a base table of a view is altered
or re-created with at least the same set of columns, then the view
can be validated. The view cannot be validated if the base table is
re-created with new columns and the view references columns no
longer contained in the re-created table. The latter point is
especially relevant in the case of views defined with a
SELECT * FROM table query, because the
defining query is expanded at view creation time and permanently
stored in the data dictionary.
|
当用户需要使用一个处于无效状态的视图时,Oracle
会在运行时自动地重新编译此视图。而当一个视图被替换(replace)后,其有效性由以下条件决定:
-
视图的定义查询中所引用的全部基表(base table)必须存在。如果视图所引用的一个基表被重命名(rename)或被移除(drop),视图将被置为无效状态且不可用。引用无效视图的语句将会失败。只有当基表恢复原名或重建后视图才能被成功编译。
-
如果基表被修改或重建后保留了原来的全部列,但是某些列的数据类型发生了变化,那么大部分依赖视图能够被成功地重新编译。
-
如果视图的基表被修改或重建后保留了原有的全部列,那么此视图的状态仍为有效。如果重建的基表中不再包含视图所引用的列,那么此视图的状态将被置为无效。如果视图是使用
SELECT * FROM table
形式的语句定义的,常会导致上述情况中的后者出现,因为在视图创建时其定义查询(defining
query)将被扩展到基表的所有字段并永久地存储于数据字典中。
|
|
029 |
Program Units and Referenced Objects
|
6.2.1.2 程序结构和引用对象
|
|
030 |
Oracle automatically invalidates a program unit when the definition of a
referenced object is altered. For example, assume that a standalone
procedure includes several statements that reference a table, a view,
another standalone procedure, and a public package procedure. In that
case, the following conditions hold:
- If the referenced table is altered,
then the dependent procedure is invalidated.
- If the base table of the referenced
view is altered, then the view and the dependent procedure are
invalidated.
- If the referenced standalone procedure
is replaced, then the dependent procedure is invalidated.
- If the body of the referenced package
is replaced, then the dependent procedure is not affected. However,
if the specification of the referenced package is replaced,
then the dependent procedure is invalidated. This is a mechanism for
minimizing dependencies among procedures and referenced objects by
using packages.
-
Whenever you create a table, index,
and view, and then drop the table, all objects dependent on that
table are invalidated, including views, packages, package bodies,
functions, and procedures.
|
当一个程序结构内的引用对象(referenced object)修改(alter)了定义之后,Oracle
自动地将此程序结构置为无效状态。例如,一个独立过程(standalone
procedure)包含的数条语句中引用了表,视图,另一个独立过程,以及一个公共包内的过程。引用对象修改后可能出现的情况如下:
- 如果引用表被修改,则依赖过程(dependent
procedure)将处于无效状态。
- 如果引用视图的基表(base
table)被修改,则此视图及依赖过程都将处于无效状态。
- 如果引用独立过程被替换(replace),则依赖过程将处于无效状态。
- 如果引用包的定义(body)被替换,则依赖过程不受影响。但是当引用包的声明(specification)被替换后,依赖过程将处于无效状态。这是一种利用包来减少过程与引用对象之间依赖性的机制。
- 当用户创建了表,索引,视图后,再将表移除(drop),所有依赖于被移除表的对象都将被置于无效状态,这些对象包括视图,包,包定义,函数,和过程。
|
|
031 |
Data Warehousing Considerations
|
6.2.1.3 数据仓库系统中的依赖性问题
|
|
032 |
Some data warehouses drop indexes on tables at night to facilitate
faster loads. However, all views dependent on the table whose index is
dropped get invalidated. This means that subsequently running any
package that reference these dropped views will invalidate the package.
|
有些数据仓库系统会在夜间移除(drop)表的索引以便加快数据加载速度。但是,所有依赖于被删除索引的表的视图将被置为无效状态。而引用了这些视图的包在运行时也将被置于无效状态。
|
|
033 |
Remember that whenever you create a table, index, and view, and then
drop the index, all objects dependent on that table are invalidated,
including views, packages, package bodies, functions, and procedures.
This protects updatable join views.
|
此处需要注意的是,当用户创建了表,并基于此表创建了索引,视图后,又移除(drop)了索引,则所有依赖于此表的对象将被置为无效状态,这包括视图,包,包定义,函数,及过程。这样做的目的是保护可更新的连接索引(updatable
join view)。
|
|
034 |
To make the view valid again, use one of the following statements:
SELECT * FROM vtest;
or
ALTER VIEW vtest compile;
|
为了使视图恢复有效,可以使用以下语句:
SELECT * FROM vtest;
或
ALTER VIEW vtest compile;
|
|
035 |
Session State and Referenced Packages
|
6.2.1.4 会话状态和引用包
|
|
036 |
Each session that references a package construct has its own instance of
that package, including a persistent state of any public and private
variables, cursors, and constants. All of a session's package
instantiations including state can be lost if any of the session's
instantiated packages are subsequently invalidated and recompiled.
|
每个会话(session)在引用一个包内程序结构(package
construct)时将创建此包的一个实例(instance),实例内包含了全部公有及私有的变量,游标,及常量的持久状态(persistent
state)。当一个会话内的包实例失效且被重新编译后,则其他所有会话内的包实例及实例状态都会丢失。
|
|
037 |
Security Authorizations
|
6.2.1.5 安全授权
|
|
038 |
Oracle notices when a DML object or system privilege is granted to or
revoked from a user or
PUBLIC and
automatically invalidates all the owner's dependent objects. Oracle
invalidates the dependent objects to verify that an owner of a dependent
object continues to have the necessary privileges for all referenced
objects. Internally, Oracle notes that such objects do not have to be
recompiled. Only security authorizations need to be validated, not the
structure of any objects. This optimization eliminates unnecessary
recompilations and prevents the need to change a dependent object's time
stamp.
|
Oracle 会监控系统中每个用户及 PUBLIC 角色的对象权限(DML
object)及系统权限(system
privilege)的授予(grant)与撤销(revoke),并自动地将相关的所有依赖对象(dependent
object)置为无效状态。之后 Oracle 会验证用户的依赖对象是否具备必要的权限来访问所需的引用对象(referenced
object)。Oracle
认为此类无效对象不需要重新编译,因为这些对象的结构没有变化,只是安全授权需要重新验证。这项优化措施避免了不必要的重新编译,也不会改变依赖对象的时间戳(time
stamp)。
|
|
039 |
See Also:
Oracle Database Application Developer's Guide - Fundamentals for
information about forcing the recompilation of an invalid view or
program unit
|
另见:
Oracle
数据库应用开发者指南 - 基础篇 了解如何强制重新编译无效的视图及程序结构
|
|
040 |
Object Name
Resolution
|
6.3 解析方案对象名称
|
|
041 |
Object names referenced in SQL statements can consist of several pieces,
separated by periods. The following describes how Oracle resolves an
object name:
- Oracle
attempts to qualify the first piece of the name referenced in the
SQL statement. For example, in hr.employees,
hr is the first piece. If there is only
one piece, then the one piece is considered the first piece.
- In the
current schema, Oracle searches for an object whose name matches the
first piece of the object name. If it does not find such an object,
then it continues with step b.
- Oracle
searches for a public synonym that matches the first piece of the
name. If it does not find one, then it continues with step c.
- Oracle
searches for a schema whose name matches the first piece of the
object name. If it finds one, then it returns to step b, now using
the second piece of the name as the object to find in the qualified
schema. If the second piece does not correspond to an object in the
previously qualified schema or there is not a second piece, then
Oracle returns an error.
If no schema is found in step c, then the object cannot be qualified and Oracle returns an error.
- A schema
object has been qualified. Any remaining pieces of the name must
match a valid part of the found object. For example, if
hr.employees.department_id is the name, then
hr is qualified as a
schema, employees is qualified as a table, and
department_id must
correspond to a column (because employees is a table). If
employees
is qualified as a package, then department_id must correspond to a
public constant, variable, procedure, or function of that package.
|
在 SQL 语句中引用的方案对象名称可由多段(piece)组成,各段之间使用“.”分隔。以下内容描述了 Oracle 如何解析对象名称:
- Oracle 首先验证
SQL 语句中所引用的对象名称的首段。例如在 hr.employees 中,hr
为首段。如果引用的名称只由一段构成,则此段就被看作是首段。
- Oracle
首先在当前方案(schema)中搜索名称与对象名首段相符的对象。如果不存在则进入到步骤 b。
- Oracle
搜索名称与对象名称首段相符的公有同义词(public synonym)。如果不存在则进入到步骤 c。
- Oracle
搜索名称与对象名称首段相符的方案。如果找到一个这样的方案,则返回步骤
b,使用对象名称的第二段在方案中搜索相符的对象。如果方案中不存在相符的对象,或者引用的对象名称只由一段构成,则 Oracle
将返回一个错误。
如果在步骤 c 中没有找到相符的方案,那么引用的对象名称也不能被验证,Oracle 将返回一个错误。-
如果数据库中存在语句里所引用的方案对象,这个方案对象还必须具备对象名称剩余段所代表的内容。例如,当引用名称为
hr.employees.department_id 时,如果
hr 代表方案名称,employees
代表表名,那么
department_id 必须与 employees
表中的某个列名称相符;如果
employees
代表包名称,那么包内必须存在名为 department_id
的公有常量,变量,过程或函数。
|
|
042 |
Because of how Oracle resolves references, it is possible for an object
to depend on the nonexistence of other objects. This situation
occurs when the dependent object uses a reference that would be
interpreted differently were another object present.
|
鉴于 Oracle 所采取的名称解析方式,有可能出现一个对象依赖于错误的引用对象(referenced
object)的情况,即一个依赖对象(dependent object)的引用可能被 Oracle 解析到一个与此依赖对象本意不同的对象上。
|
|
043 |
See Also:
Oracle Database Administrator's Guide
|
另见:
Oracle
数据库管理员指南
|
|
044 |
Shared SQL
Dependency Management
|
6.4 共享 SQL 的依赖性管理
|
|
045 |
In addition to managing dependencies among schema objects, Oracle also
manages dependencies of each shared SQL area in the shared pool. If a
table, view, synonym, or sequence is created, altered, or dropped, or a
procedure or package specification is recompiled, all dependent shared
SQL areas are invalidated. At a subsequent execution of the cursor that
corresponds to an invalidated shared SQL area, Oracle reparses the SQL
statement to regenerate the shared SQL area.
|
Oracle 除了需要管理方案对象(schema object)的依赖性,还需管理共享池(shared pool)中各个共享 SQL
区(shared SQL area)的依赖性。如果用户创建,修改或移除了表,索引,同义词,或序列,或者重新编译了包,或包声明,那么所有依赖共享
SQL 区都将被置为无效。当一个基于无效共享 SQL 区的游标继续执行时,Oracle 将重新对 SQL 语句进行语法分析,并生成新的共享
SQL 区。
|
|
046 |
Local and Remote
Dependency Management
|
6.5 本地及远程依赖性管理
|
|
047 |
Tracking dependencies and completing necessary recompilations are
performed automatically by Oracle. Local dependency management occurs
when Oracle manages dependencies among the objects in a single database.
For example, a statement in a procedure can reference a table in the
same database.
|
监控数据库内的依赖性以及进行必要的重编译都是由 Oracle 自动地执行的。本地依赖性管理(local dependency
management)是指 Oracle 管理一个单一数据库内各个对象间的依赖关系。例如,某过程内的一个 SQL
语句引用了相同数据库中的一个数据表。
|
|
048 |
Remote dependency management occurs when Oracle manages dependencies in
distributed environments across a network. For example, an Oracle Forms
trigger can depend on a schema object in the database. In a distributed
database, a local view's defining query can reference a remote table.
|
远程依赖性管理(remote dependency management)是指 Oracle 管理一个分布式环境内的各种依赖关系。例如,一个
Oracle Forms 触发器可以依赖于一个数据库内的方案对象;在一个分布式数据库内,一个本地视图的定义查询可以引用一个远程表。
|
|
049 |
Management of Local Dependencies
|
6.5.1 本地依赖性管理
|
|
050 |
Oracle manages all local dependencies using the database's internal
dependency table, which keeps track of each schema object's dependent
objects. When a referenced object is modified, Oracle uses the
depends-on table to identify dependent objects, which are then
invalidated.
|
Oracle 使用数据库内部的依赖关系表(dependency
table)来管理所有的本地依赖性,依赖关系表用于记录每个方案对象的依赖对象(dependent
object)。当用户修改了一个引用对象(referenced object),Oracle
就会使用依赖关系表确定此对象的所有依赖对象,并将她们全部置为无效状态。
|
|
051 |
For example, assume a stored procedure UPDATE_SAL
references the table JWARD.employees. If
the definition of the table is altered in any way, the status of every
object that references JWARD.employees is
changed to INVALID, including the stored
procedure UPDATE_SAL. As a result, the
procedure cannot be run until it has been recompiled and is valid.
Similarly, when a DML privilege is revoked from a user, every dependent
object in the user's schema is invalidated. However, an object that is
invalid because authorization was revoked can be revalidated by
"reauthorization," in which case it does not require full recompilation.
|
例如,假设存储过程 UPDATE_SAL
引用了 JWARD.employees 表。当 JWARD.employees
表的定义被修改后,所有引用此表的对象都将被置为 INVALID,包括存储过程 UPDATE_SAL。此存储过程必须经过重新编译并置为有效状态后才能再次运行。同样,当一个用户所拥有的对象权限(DML
privilege)被撤销(revoke)后,此用户方案内的所有依赖对象也将被置为无效状态。但在后种情况中,由于使对象无效的原因是授权(authorization)被撤销,因此可以通过重新授权(reauthorization)使对象恢复有效状态,此时无需对无效对象进行重编译操作。
|
|
052 |
Management of Remote Dependencies
|
6.5.2 远程依赖性管理
|
|
053 |
Oracle also manages application-to-database and distributed database
dependencies. For example, an Oracle Forms application might contain a
trigger that references a table, or a local stored procedure might call
a remote procedure in a distributed database system. The database system
must account for dependencies among such objects. Oracle uses different
mechanisms to manage remote dependencies, depending on the objects
involved.
|
Oracle 还要管理应用程序与数据库间的依赖关系,以及分布式数据库间的依赖关系。例如,Oracle Forms
应用程序可以使用一个引用了数据表的触发器;本地的存储过程也可能调用分布式数据库系统中的远程过程。数据库系统必须能够管理此类对象间的依赖关系。Oracle
根据对象的不同而选择不同的机制来管理远程依赖性。
|
|
054 |
Dependencies Among Local and Remote Database Procedures
|
6.5.2.1 本地过程及远程过程间的依赖性
|
|
055 |
Dependencies among stored procedures including functions, packages, and
triggers in a distributed database system are managed using time
stamp checking or signature checking.
|
在分布式数据库系统中,函数,包,触发器等存储过程间的依赖性是通过时间戳检查(time
stamp checking)或特征标识检查(signature checking)来进行管理的。
|
|
056 |
The dynamic initialization parameter
REMOTE_DEPENDENCIES_MODE determines whether time stamps or
signatures govern remote dependencies.
|
动态初始化参数
REMOTE_DEPENDENCIES_MODE 用于决定使用哪种方式来管理远程依赖性。
|
|
057 |
See Also:
Oracle Database Application Developer's Guide - Fundamentals for
details about managing remote dependencies with time stamps or
signatures
|
另见:
Oracle
数据库应用开发者指南 - 基础篇 了解利用时间戳及特征标识管理远程依赖性的详细信息。
|
|
058 |
Time stamp Checking
|
6.5.2.1.1 时间戳检查
|
|
059 |
In the time stamp checking dependency model, whenever a procedure is
compiled or recompiled its time stamp (the time it is created,
altered, or replaced) is recorded in the data dictionary. The time stamp
is a record of the time the procedure is created, altered, or replaced.
Additionally, the compiled version of the procedure contains information
about each remote procedure that it references, including the remote
procedure's schema, package name, procedure name, and time stamp.
|
在时间戳检查模式下,一个过程被编译或重编译时的时间戳(即一个过程被创建,修改或替换的时间)将被记录在数据字典中。同时还将记录此过程的版本信息,包括此过程所引用的所有远程过程的所属方案,包名称,过程名称,及时间戳。
|
|
060 |
When a dependent procedure is used, Oracle compares the remote time
stamps recorded at compile time with the current time stamps of the
remotely referenced procedures. Depending on the result of this
comparison, two situations can occur:
- The local and remote procedures run
without compilation if the time stamps match.
- The local procedure is invalidated if
any time stamps of remotely referenced procedures do not match, and
an error is returned to the calling environment. Furthermore, all
other local procedures that depend on the remote procedure with the
new time stamp are also invalidated. For example, assume several
local procedures call a remote procedure, and the remote procedure
is recompiled. When one of the local procedures is run and notices
the different time stamp of the remote procedure, every local
procedure that depends on the remote procedure is invalidated.
|
当运行一个依赖过程时,Oracle 将对此过程编译时所记录的远程时间戳与远程引用对象当前的时间戳进行比较。根据比较结果,可能有两种情况发生:
- 如果时间戳比较结果一致,那么本地及远程过程均无需编译就可直接运行。
-
如果存在时间戳比较结果不一致的远程引用对象,那么本地过程将被置为无效状态,并向此过程的调用者发送一个错误信息。此后,Oracle
还会将所有引用了时间戳发生变化的远程过程的本地过程置为无效状态。例如,多个本地过程中都需调用一个远程过程,且此远程过程进行了重编译。当一个本地过程开始运行,并发现远程过程的时间戳有变后,所有依赖于此远程过程的本地过程都将被置为无效状态。
|
|
061 |
Actual time stamp comparison occurs when a statement in the body of a
local procedure runs a remote procedure. Only at this moment are the
time stamps compared using the distributed database's communications
link. Therefore, all statements in a local procedure that precede an
invalid procedure call might run successfully. Statements subsequent to
an invalid procedure call do not run at all. Compilation is required.
|
实际上,时间戳的比较发生在本地过程中调用远程过程的语句执行时。此时 Oracle 才会使用分布式数据库的通信链接(communications
link)对两个时间戳进行比较。因此,本地过程中位于无效远程过程调用之前的语句可能全部运行正常,而之后的语句则根本不会运行。此时必须对本地过程进行重编译。
|
|
062 |
Depending on how the invalid procedure is called, DML statements run
before the invalid procedure call are rolled back. For example, in the
following, the UPDATE results are rolled
back as the complete PL/SQL block changes are rolled back.
|
无效远程过程调用之前的 DML 语句是否被回滚,是由此无效远程过程的调用方式决定的。例如,在以下代码中,UPDATE
语句的结果将被回滚,整个 PL/SQL 块内发生的数据修改都将被回滚。
|
|
063 |
BEGIN
UPDATE table set ...
invalid_proc;
COMMIT;
END;
|
BEGIN
UPDATE table set ...
invalid_proc;
COMMIT;
END;
|
|
064 |
However, with the following, the UPDATE
results are final. Only the PROC call is
rolled back.
|
但是,在以下代码中,UPDATE 语句的结果将被写入数据库中。只有过程调用将被回滚。
|
|
065 |
UPDATE table set ...
EXECUTE invalid_proc;
COMMIT;
|
UPDATE table set ...
EXECUTE invalid_proc;
COMMIT;
|
|
066 |
Signature Checking
|
6.5.2.1.2 特征标识检查
|
|
067 |
Oracle provides the additional capability of remote dependencies using
signatures. The signature capability affects only remote
dependencies. Local dependencies are not affected, as recompilation is
always possible in this environment.
|
用户还可以使用
Oracle 提供的特征标识(signature)功能来管理远程依赖性。特征标识功能只对远程依赖性管理有效。本地依赖性无需使用特征标识进行管理,因为在本地环境中无效对象可以随时被重编译[在远程环境中无此便利条件,因此使用特征标识管理依赖性,与
使用时间戳相比要求较为宽松]。
|
|
068 |
The signature of a procedure contains information about the following
items:
- Name of the package, procedure, or
function
- Base types of the parameters
- Modes of the parameters (IN,
OUT, and IN OUT)
|
一个过程的特征标识中包含以下信息:
- 包,过程,或函数的名称
- 参数的类型
- 参数的模式 (IN,OUT,和 IN OUT)
|
|
069 |
Note:
Only the types and modes of parameters are significant. The name of
the parameter does not affect the signature.
|
提示:
只有参数的类型和模式是有意义的。参数的名称不会对特征标识有影响。
|
|
070 |
If the signature dependency model is in effect, a dependency on a remote
program unit causes an invalidation of the dependent unit if the
dependent unit contains a call to a procedure in the parent unit, and
the signature of this procedure has been changed in an incompatible
manner. A program unit can be a package, stored procedure, stored
function, or trigger.
|
在特征标识依赖模型(signature dependency model)生效后,如果一个依赖程序结构(dependent
unit)中调用了引用程序结构(referenced unit)内的过程,且此过程的特征标识发生了不兼容性(incompatible
manner)的变化,则此依赖程序结构在运行时将会被置为无效。上述的程序结构可以是包,存储过程,函数或触发器。
|
|
071 |
Dependencies Among Other Remote Schema Objects
|
6.5.2.2 其他远程方案对象的依赖性
|
|
072 |
Oracle does not manage dependencies among remote schema objects other
than local-procedure-to-remote-procedure dependencies.
|
除了本地过程引用远程过程造成的依赖性问题之外,Oracle 不会管理其他由于远程方案对象造成的依赖性问题。
|
|
073 |
For example, assume that a local view is created and defined by a query
that references a remote table. Also assume that a local procedure
includes a SQL statement that references the same remote table. Later,
the definition of the table is altered.
|
例如,一个本地视图的定义查询中引用了一个远程表,且一个本地过程的 SQL
语句中也引用了相同的远程表。在某一时刻,远程表的定义被修改(alter)了。
|
|
074 |
As a result, the local view and procedure are never invalidated, even if
the view or procedure is used after the table is altered, and even if
the view or procedure now returns errors when used. In this case, the
view or procedure must be altered manually so that errors are not
returned. In such cases, lack of dependency management is preferable to
unnecessary recompilations of dependent objects.
|
在远程表的定义被修改后使用本地视图或过程,甚至在使用过程中返回了错误,本地视图及过程都不会被置为无效状态。在这种情况下,必须手工修改视图或过程的定义才能避免错误发生。这样处理依赖性问题能够避免对依赖对象进行不必要的编译。
|
|
075 |
Dependencies of Applications
|
6.5.2.3 应用程序的依赖性
|
|
076 |
Code in database applications can reference objects in the connected
database. For example, OCI and precompiler applications can submit
anonymous PL/SQL blocks. Triggers in Oracle Forms applications can
reference a schema object.
|
数据库应用程序的代码中也会引用相关数据库中的对象。例如,在 OCI 及预编译应用程序中可以提交匿名 PL/SQL 块。Oracle Forms
应用程序中的触发器也可以引用方案对象。
|
|
077 |
Such applications are dependent on the schema objects they reference.
Dependency management techniques vary, depending on the development
environment.
|
这些应用程序依赖于她们所引用的方案对象。依赖性管理的方式依据开发环境的不同而不同。
|
|
078 |
See Also:
Manuals for your application development tools and your operating
system for more information about managing the remote dependencies
within database applications
|
另见:
应用开发工具手册及操作系统文档了解如何管理数据库应用程序内的远程依赖性
|



